Modeling
Air quality affects everyone's health and well-being, yet the factors influencing it can be complex. Air quality modeling offers a way to understand and predict the quality of the air we breathe. Here’s a simplified guide to what air quality modeling is all about:
What is Air Quality Modeling?
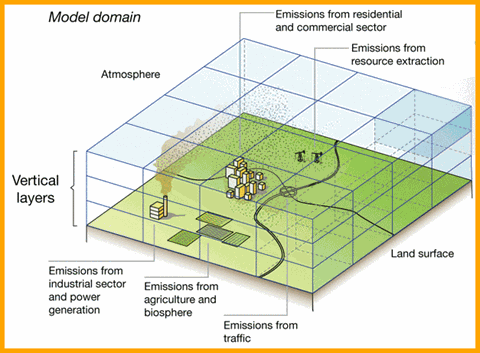
Air quality modeling is a scientific tool used to estimate how pollutants disperse in the atmosphere. Think of it like a virtual simulation that helps us understand how various factors, such as emissions from vehicles, industries, and natural sources, affect the air we breathe.
There are two types of models we can use for understanding air quality: photochemical modeling and dispersion modeling. Photochemical modeling simulates the changes of pollutant concentrations in the atmosphere to help tell us which emissions sources contribute to ozone concentrations at violating monitors.
Dispersion modeling tells us how a pollutant will spread out from its emission source. Imagine you're baking cookies and you want to know how the smell spreads throughout your house. You might consider factors like how many cookies you bake, how big your kitchen is, and whether you've opened a window. Dispersion modeling works similarly, but with much more complexity and precision. Scientists input data about emissions (like exhaust from cars), weather patterns, geography, and other factors into computer programs. These programs then simulate how pollutants move, react, and disperse in the atmosphere over time.
Dispersion modeling NOT appropriate tool for ozone. Photochemical modeling is a more appropriate tool for secondary pollutants like ozone because it includes chemical reactions. Photochemical modeling is used for our ozone State Implementation Plan (SIP) to show the EPA whether all our control strategies will be enough to achieve attainment of the federal standards. Dispersion modeling is used for permitting requirements.
The Weld County monitoring data is being processed for dispersion modeling by the Permit Modeling Unit at the Air Pollution Control Division (APCD) for Colorado.
Why is modeling important?
Air quality modeling helps us understand the potential impacts of pollution on human health and the environment. By predicting where pollutants are likely to accumulate, we can take steps to reduce emissions and protect vulnerable populations.
For example, if a state wants to build a new highway, air quality modeling can help predict how this might affect pollution levels in nearby neighborhoods. This information can then be used to make informed decisions about where to place the highway and what measures to take to mitigate pollution.
Limitations
 While air quality modeling is a powerful tool, it's not without limitations. The accuracy of the models depends on the quality of the data and the assumptions made by scientists. Factors like sudden changes in weather or unexpected emissions can also affect the accuracy of predictions.
While air quality modeling is a powerful tool, it's not without limitations. The accuracy of the models depends on the quality of the data and the assumptions made by scientists. Factors like sudden changes in weather or unexpected emissions can also affect the accuracy of predictions.
Additionally, air quality models are constantly evolving as scientists improve their understanding of atmospheric processes and gather more data. This means that while models provide valuable insights, they should be used as tools to inform decision-making rather than as crystal balls for predicting the future with absolute certainty.